Understanding the Core of Agile Methodology: Scrum and Kanban in Software Development
Preface
Agile methodology is a design operation approach that emphasizes inflexibility, communication, and collaboration. Its core principles are grounded on the Agile Manifesto, which values individualities and relations, working software, client collaboration, and responding to change.
Two popular fabrics of Agile methodology are Scrum and Kanban. In this blog post, we will bandy the core principles of Scrum and Kanban, their differences, and how they can be used in different types of systems.
Scrum
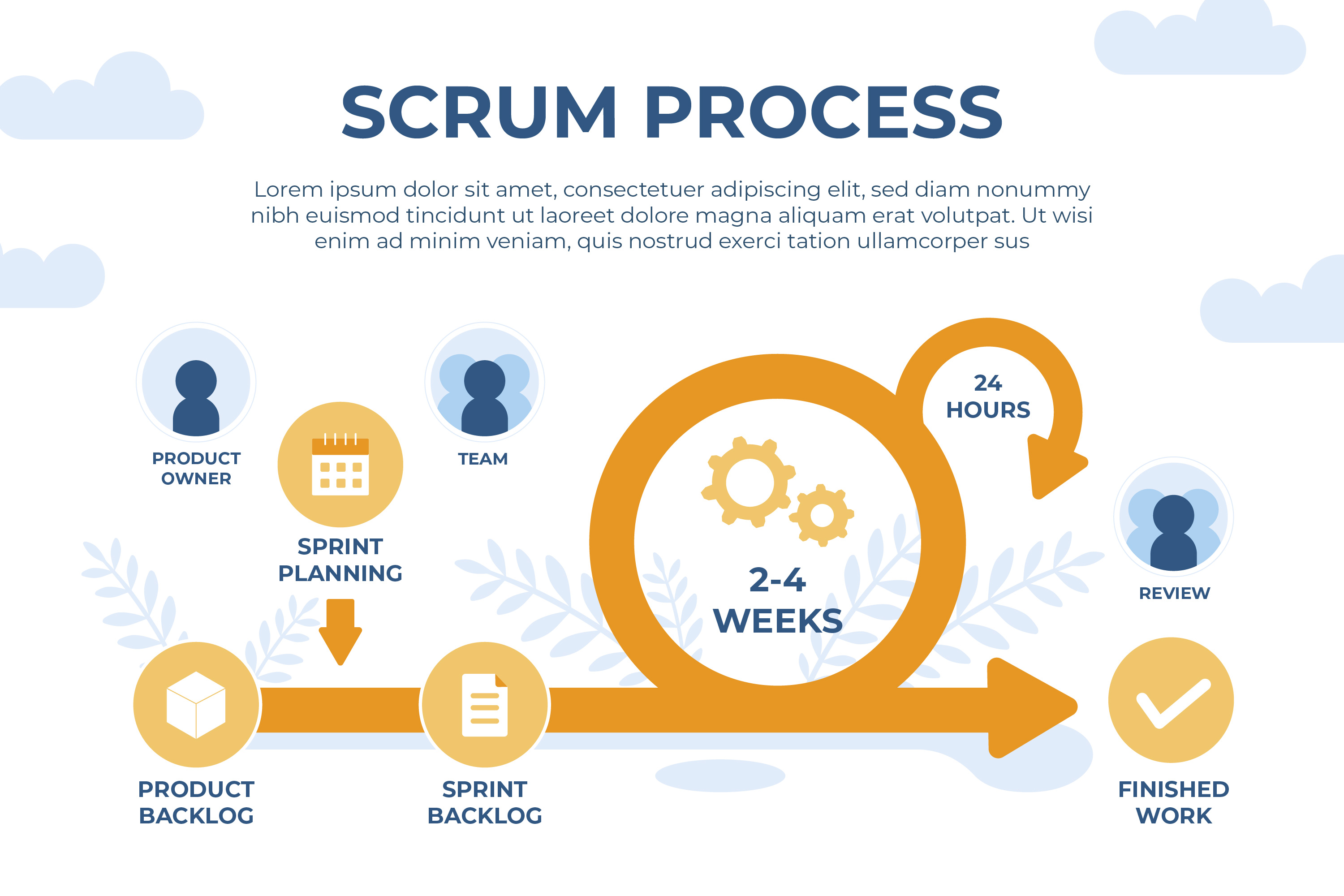
Scrum is a frame that emphasizes cooperation, responsibility, and iterative progress toward a well- defined thing. It's used for systems that bear a high degree of inflexibility and rigidity, where the conditions aren't completely understood or may change constantly.
The core principles of Scrum include
* Sprints Scrum systems are broken down into sprints, which are fixed time ages( generally 2- 4 weeks) where a specific set of tasks must be completed.
* places Scrum brigades correspond of three places the product proprietor, the Scrum master, and the development platoon. Each part has specific liabilities and is responsible for the success of the design.
* Vestiges Scrum systems have three vestiges the product backlog, the sprint backlog, and the proliferation. These vestiges help track progress, prioritize tasks, and insure translucency.
* Events Scrum events include sprint planning, diurnal stage- ups, sprint reviews, and sprint retrospectives. These events help the platoon stay focused, communicate effectively, and continuously ameliorate.
Kanban
Kanban is a frame that focuses on imaging work, limiting work in progress, and optimizing inflow. It's used for systems that have a well- defined workflow and bear a high degree of effectiveness and quality. The core principles of Kanban include
* Visual boards Kanban systems use visual boards to track progress and give translucency. These boards generally include columns for each stage of the workflow and cards to represent tasks.
* Work in progress( WIP) limits Kanban systems limit the quantum of work in progress to optimize inflow and help overfilling the platoon. This helps insure that tasks are completed efficiently and with high quality.
* nonstop enhancement Kanban systems continuously ameliorate by assaying data, relating backups, and making incremental changes to the workflow.
* Pull system Kanban systems use a pull system, where tasks are pulled from a backlog only when there's capacity to work on them. This helps help overfilling the platoon and ensures that tasks are completed in the right order.
Scrum vs. Kanban
While Scrum and Kanban partake some parallels, similar as emphasizing collaboration and nonstop enhancement, they've some crucial differences. Scrum is best suited for systems with a high degree of query and change, while Kanban is best suited for systems with a well- defined workflow and a focus on effectiveness. Scrum uses fixed- length sprints and has a more restricted structure, while Kanban is more flexible and allows for nonstop inflow. Scrum brigades have specific places and events, while Kanban brigades are more tone- organizing and have smaller formal events.
Conclusion
Agile methodology is a important approach to design operation that emphasizes inflexibility, collaboration, and nonstop enhancement. Scrum and Kanban are two popular fabrics of Agile methodology that have different strengths and are suited for different types of systems. By understanding the core principles of Scrum and Kanban, design directors can choose the right frame for their design and help their platoon deliver high- quality results.


Comments
Post a Comment